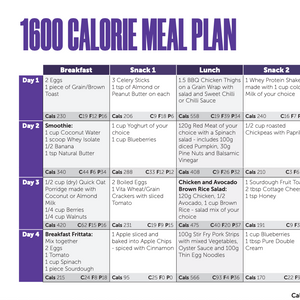
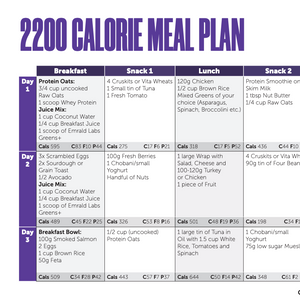
Collection: Creatine Monohydrate
Buy Creatine Monohydrate at Elite Supps Australia
Creatine monohydrate is a scientifically endorsed supplement recognised for enhancing muscular strength and endurance during workout sessions lasting under 3 minutes (1, 2). More than 700 human studies have investigated the safety and efficacy of creatine, solidifying its status as the most comprehensively researched supplement aimed at muscle improvement.
What is creatine monohydrate?
Creatine monohydrate is an amino acid which is found naturally in muscle cells. Creatine can be found in food sources such as beef and salmon, however, creatine powder supplements allow for a convenient source and higher dose. For example, in order to get the equivalent dose of 1 tsp of creatine monohydrate powder from food, you would have to eat 1 kilogram of raw beef! Furthermore, food sources of creatine lose most of their creatine content during cooking as the cooking of the meat will denature the creatine protein. In essence, a convenient cost effective source of creatine can be found in supplements.
How does creatine monohydrate work?
Creatine monohydrate works by increasing energy availability during short bursts of activity. It helps with ATP production, which is the main energy currency of the human body. By ensuring creatine stores are saturated, this means more energy is available to you while you are working through a set of bench press or squats. Creatine has been shown to increase maximal muscle strength and power by 5 to 15% (3).
Essentially, creatine supplementation allows you to push out more reps and more weight when in the gym. Just one week of creatine supplementation can enhance muscle performance (4).
Creatine can also assist with body composition and increasing lean muscle mass due to the hypertrophy of the muscles. It is important to note that this is a flow-on effect from training hard in the gym with progressive overload and effective programming.
There is now early research showing potential benefits to cognitive and brain health with creatine supplementation. Currently there is evidence to show that creatine supplementation may improve short term memory (5).
Compare creatine monohydrate supplements at Elite Supps
With so many creatine supplements available in the market, it’s important to take creatine from a high quality and reputable source.
-
Emrald Labs Creatine (Emrald Labs’ high quality creatine comes in convenient 100g and 250g sizes, along with cost effective 500g and 1kg sizes!)
-
EHP Crea-8 (This creatine is premium german grade creatine which ensures no bloating. EHP’s Crea-8 is pharmaceutical grade 100% pure creatine. This 500g tub will provide you with 100 servings of creatine.)
-
Switch Creatine (This creatine is micronised which makes it easier to dissolve in water. Switch’s creatine is HPLC tested to ensure quality and efficacy.)
-
ON Micronized Creatine Powder (Optimum Nutrition’s creatine is also micronized to make it easier to dissolve and digest with water. This is also Banned Substance Tested in accordance with the Informed Choice certification.)
Aside from our Top 10 recommendations, you can also find the right creatine monohydrate supplements by checking out customer reviews. Look for comments on pharmaceutical grade, mixability, and quantity options to find the right creatine supplement for you.
Enjoy great deals on creatine monohydrate supplements with Elite Supps
At Elite Supps, we're all about delivering premium creatine monohydrate supplements at affordable prices. In addition to ongoing deals and exclusive discounts up to 80% off, we also offer a wide range of supplement brands so you can find the perfect creatine product for you.
Looking for a specific creatine product or simply want some assistance with your shopping? Feel free to contact our customer service team for any enquiries you may have!
FAQ
How much creatine should I take?
There's a low risk of side effects when taking creatine. A systematic review and meta analysis showed that creatine supplementation does not induce renal damage (86">7, 8). However, it's worth noting that there are no long-term studies on creatine side effects yet due to the newness of the supplement.
To avoid adverse effects (especially if you're an athlete), it may be wise to take a HASTA-certified creatine. Always speak to a healthcare professional if you're concerned about potential side effects or want to take creatine while pregnant or breastfeeding.
There are many factors involved with weight fluctuations, therefore it cannot conclusively be said if creatine supplementation will make you gain or lose weight. However, creatine supplementation may improve physique appearance and body composition due to two mechanisms. First, creatine supplementation can increase muscle size by assisting with hypertrophy (growing the muscle) and with cellular swelling. Creatine causes cells to swell as it pulls water into the cell when it is absorbed.
This makes muscles appear more full and bubbly! These factors may increase the weight on the scale, but not because creatine is causing body fat gain. Second, increasing muscle size and strength may increase basal metabolic rate, allowing the body to burn more calories at rest by simply existing. This may cause the scales to fall, as your body is more efficiently burning calories. The combination of these mechanisms can assist with building the appearance of a more favourable physique.
References
1: Creatine Supplementation and Lower Limb Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Charlotte Lanhers, Bruno Pereira, Geraldine Naughton, Marion Trousselard, François-Xavier Lesage & Frédéric Dutheil Sports Medicine volume 45, pages1285–1294 (2015). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40279-015-0337-4
2: Creatine Supplementation and Upper Limb Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Charlotte Lanhers, Bruno Pereira, Geraldine Naughton, Marion Trousselard, François-Xavier Lesage & Frédéric Dutheil Sports Medicine volume 47, pages163–173 (2017). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40279-016-0571-4
3: Effects of creatine supplementation on performance and training adaptations. Richard B Kreider PMID: 12701815https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12701815/
4: Creatine supplementation enhances muscular performance during high-intensity resistance exercise, J S Volek 1, W J Kraemer, J A Bush, M Boetes, T Incledon, K L Clark, J M Lynch Affiliations expand, PMID: 9216554 DOI: 10.1016/S0002-8223(97)00189-2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9216554/
5: Effects of creatine supplementation on cognitive function of healthy individuals: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Author links open overlay panel Konstantinos I.AvgerinosabNikolaosSpyrouacKonstantinos I.BougioukasbDimitriosKapogiannisd https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0531556518300263
6: International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine Richard B Kreider 1, Douglas S Kalman 2, Jose Antonio 3, Tim N Ziegenfuss 4, Robert Wildman 5, Rick Collins 6, Darren G Candow 7, Susan M Kleiner 8, Anthony L Almada 9, Hector L Lopez 4 10 PMID: 28615996 PMCID: PMC5469049 DOI: 10.1186/s12970-017-0173-zhttps://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28615996/
7: Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Renal Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Alexandrede Souza e SilvaPhD∗AdrianaPertillePhD†Carolina GabrielaReis BarbosaMSc†JasieleAparecida de Oliveira SilvaMSc∗‡Diego Vilelade JesusPE∗Anna Gabriela Silva VilelaRibeiroMSc†Ronaldo JúlioBaganhaPhD∗José Jonasde OliveiraMSc∗† https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1051227619302286
8: Long-term creatine supplementation does not significantly affect clinical markers of health in athletes. March 2003Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 244(1-2):95-104, DOI:10.1023/A:1022469320296, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/10798700_Long-term_creatine_supplementation_does_not_significantly_affect_clinical_markers_of_health_in_athletes